Having control over an administrator account allows you to do certain things, and also you will have the administrator privileges on the system, which gives you an extra advantage over all other users on the system. It is very easy to control the user’s log in time in that system by using command prompt . When a deadline for a particular user is established, the user can only access the system in that particular period .
Steps To Control The User Login Time :
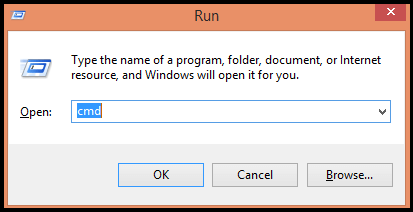
Step 1 : Open Command Prompt :
You open it by just simply entering ” cmd ” in your window’s search box Or press ” Windows + R ” ( Run dialog box will be displayed ) and type “ cmd ” in it .
Step 2 : Use Syntax :
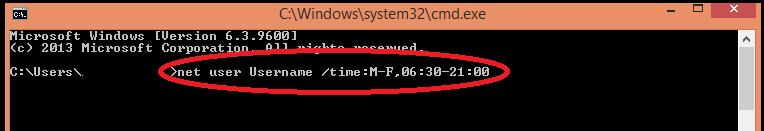
” net user ” is the syntax to set the login time.
- Type in ” net user Username /time:M-F,06:30-21:00 ” .This is the syntax to set the login times for a week .
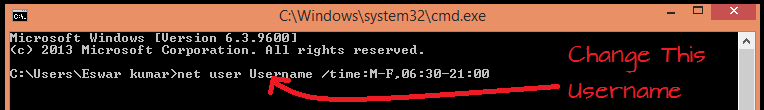
- Replace the word username with any registered username on your computer. This means that the selected user has access to his account ; Monday- Friday from 8:00 a.m. – 9:00 p.m .
- Hit enter.
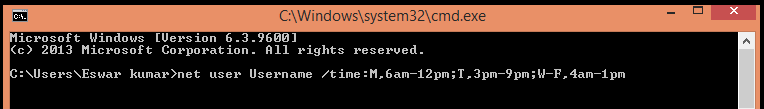
Step 3 : Specifying Different Times Daily :
You can also use the below given form for specifying different times daily.
- Go to the command prompt as shown above.
- Enter ” net user Username /time:M,6am-12pm;T,3pm-9pm;W-F,4am-1pm “. This method allows you to set the allocation to the user in different ways for each day. You can do the same by simply entering the day, followed by a comma , and the time range , and a semicolon .
Tips :
- You can specify the time in military format as 18:00-24: 00 or you can also use the standard time format as 6:00 am – 9:00 pm .
- If you want to have a user with complete login time for every day of the week, then simply write the syntax like: ” net user Username /time:all ” .